Low Cholesterol Levels Associated with 990% Higher Mortality After Heart Attack
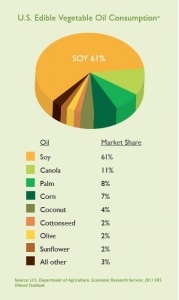
A 2015 study in Critical Care Medicine is titled, “Lipid Paradox in Acute Myocardial Infarction- The Association with 30-Day In-Hospital Mortality.” This study followed 724 hospitalized patients who suffered an acute heart attack (i.e., myocardial infarction). The scientists attempted to clarify the relationship between the lipid profiles and the 30-day mortality in patients who suffered a heart attack. The authors found that those with lower LDL-cholesterol and triglyceride levels had a significantly elevated mortality risk when compared to patients with higher LDL-cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Why would lowered cholesterol and triglyceride levels be associated with a higher mortality rate? Fats from triglycerides are a major energy source and LDL-cholesterol is critical for cell membrane synthesis and is needed to fight infections. Adequate LDL-cholesterol and triglyceride levels may be critical for cell function and survival in the case of a heart attack—as well as in other conditions. Folks, we have been hoodwinked to believe that we must all take cholesterol-lowering medications in order to prevent and/or treat heart disease. People do not get heart disease because their cholesterol level is elevated. Remember, 50% of patients who suffer a heart attack have normal cholesterol levels.